A team of scientists scrambles to better understand a gigantic cloud of methane looming over the Four Corners region of the U.S. Southwest. This single cloud is believed to comprise nearly 10 percent of all methane emissions derived from natural gas in the United States. But its origins remain a mystery. The following article on the subject from pbs.org was written by Laura Santhanam and posted June 3, 2015 with the title “Why Is There a Huge Methane Hotspot in the American Southwest?”
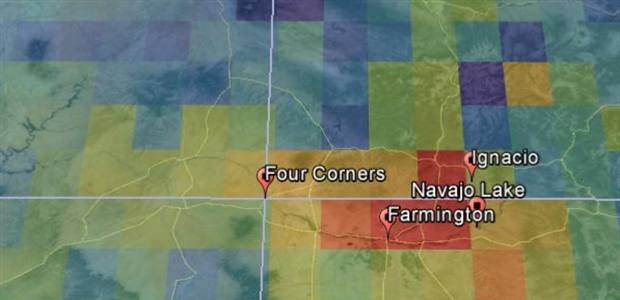
The Four Corners region of the southwest United States is a magnificent, otherworldly place, marked by red rock vistas, ancient cliff dwellings and sweeping blue sky. The names alone paint a picture of the landscape: The Painted Desert. The Petrified Forest. Monument Valley. But billowing above the rust-colored earth is the country’s largest concentration of methane, according to satellite data. That’s because this spot where Utah, Colorado, Arizona and New Mexico meet is also home to one of the nation’s most productive natural gas fields and coalbed methane basins. About 10 percent of the country’s estimated methane emissions from natural gas is found in this region, according to recent scientific research and the Environmental Protection Agency.
Methane is odorless, colorless and invisible to the naked eye. Following carbon dioxide, methane ranks as the second most prevalent greenhouse gas emitted by human activity in the United States. But in the short term, atmospheric methane is more than 100 times more potent than carbon dioxide at holding the sun’s heat, according to Colm Sweeney, the lead scientist for the NOAA Earth System Research Lab Aircraft Program. “It’s a very strong greenhouse gas and traps heat really effectively,” he said. “It’s like putting an inch of insulation in your attic versus putting 100 inches of insulation in your attic with the same amount of CO2.”
Scientists first realized methane was flooding the Four Corners after a satellite in 2003 detected higher-than normal amounts of the gas. A year earlier, the European Space Agency had launched Envisat, an eight-ton, sun-powered satellite the size of a school bus. While orbiting the planet, its mission was to track ocean temperature and ozone depletion, improving environmental studies. Onboard was SCIAMACHY, an image spectrometer that monitored gases in the Earth’s atmosphere, including methane, and created novel data maps. For years, the satellite captured images of sunlight reflecting off the Earth’s surface. Absorptions of methane in the data revealed its distribution around the globe.
But one day in April 2012, for reasons still unclear, ESA ground control crews lost all contact with Envisat and its instruments. The satellite had disappeared, but the data remained. In that data, Christian Frankenberg, a scientist with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, found what he initially thought might be an error. A startling red spot of methane hovered over the U.S. Southwest, burning brighter, he said, than any other hotspot in the United States.
Atmospheric scientist Eric Kort of the University of Michigan plumbed the data further, using satellite images produced between 2003 and 2009. The team collected air samples, conducted on-the-ground observations, performed simulations and analyzed readings before concluding that the methane floating above the Four Corners represented the country’s largest concentration of the gas. In findings they published in October in the journal Geophysical Research Letters, the scientists also suggested that the EPA was underestimating methane emissions nationwide, including in the Four Corners. Still, they puzzled over the source of the hotspot.
The Four Corners is part of the San Juan Basin, a region that covers 7,500 square miles and is “the most productive coalbed methane basin in North America,” according to the EPA. For years, oil and gas companies have tapped into this massive energy stash in the middle of the desert. About 60,000 wells are scattered across the area.
But scientists don’t understand how such massive amounts of methane are getting released into the air. Is it coming from natural sources, like the exposed coal seam jutting above the earth’s surface in parts of the San Juan Basin? Is it coming from open mine shafts or leaking equipment that belongs oil and gas companies? Is it a combination of these factors, or none of these factors? “The interesting part of the Four Corners is that there’s a lot of stuff coming out of these coal beds. I’m not going to say natural because we’re not sure how much that is going into production is influencing how much seepage is coming up,” Sweeney said.
Methane is generally harmless, but it can be problematic when it exists in extremely dense quantities or confined areas. Under sustained conditions for a long period of time, studies have found that people may have trouble breathing or even lose consciousness. In cramped spaces like a coal mine, methane is dangerous and can ignite easily. That’s where the term “canary in a coal mine” came from. If a caged canary in a mineshaft stopped singing and died, that signaled that there was too little oxygen and too much methane, carbon monoxide and other gases, and miners needed to get out, stat. That’s also why coal mines typically pump fresh air into the shaft and use ventilation systems to dilute the gas.
Often when industrial sources emit methane, they also release volatile organic compounds into the air, said Mary Uhl, an environmental protection specialist with the federal Bureau of Land Management. These compounds trigger chemical reactions that create ozone, which can harm people with asthma or respiratory conditions. Ozone levels in the Four Corners hover at 0.071 parts per million, which means they just barely meet the Environmental Protection Agency’s national air quality standards of 0.075 parts per million. And if federal standards drop to 0.065 to 0.070 parts per million, as proposed, the Four Corners would no longer meet the legal rate.
That’s a problem normally seen in urban areas with far more people and cars than what you would find in the Four Corners, Uhl said. “Rural areas of the country haven’t typically bumped up against the federal air quality standard for ozone,” she said. A reduction in methane emissions would likely reduce volatile organic compounds along with ozone levels, Uhl said.
In April, a team of scientists traveled to the Four Corners to study methane in this region. They flew five aircraft with equipment designed to detect the gas and drove two research vehicles roughly 3,000 miles — the distance between Los Angeles and Portland, Maine. Ultimately, they collected hundreds of air samples of methane that will be analyzed for 55 different trace gases and two methane isotopes. Now the scientists are sifting through terabytes of data, searching for answers. Air samples must be analyzed, and maps studied further to identify the origins of the gas. “This is where the detective work comes in, and where the fun of it comes in,” Sweeney with NOAA said. It will take months, but Frankenberg said he hopes that the team can produce findings by the end of the year. “It’s really rare that we get to observe an anomaly like this, but at the same time have measurements on the ground that confirm it,” he said.
Meanwhile, people who live in the Four Corners have mobilized to address the issue. Residents in the region have long reported respiratory problems. High ozone days when ground-level ozone blankets parts of the region are not uncommon, and lead to frequent emergency room visits. Community and government leaders have formed the Four Corners Air Quality Group, which meets periodically to figure out how to mitigate the effects of methane and the ozone that its presence aggravates.
San Juan County, which is in the affected area, got a C grade for ozone-related air quality, according to the American Lung Association’s 2015 State of the Air report. But the link between ozone and respiratory problems extends beyond the Four Corners region. Studies have shown that visits to the emergency room for asthma are more frequent on high-ozone days, according to the EPA. Those with asthma may be more sensitive to ozone, this online report states, and “the injury, inflammation, and increased airway reactivity induced by ozone exposure may result in a worsening of a person’s underlying asthma status, increasing the probability of an asthma exacerbation or a requirement for more treatment.”
About 200 people attended a public forum in San Juan County’s city of Farmington in April. Participants included members of the oil and gas industry, the local scientific community, nearby tribal communities and the general public. Julia Madrid, 31, a baker in Durango, Colorado, was among them. She suffers from lupus and said she has wondered if the region’s air has aggravated her illness. Her mother alerted her to a map of the region’s methane hotspot in the local newspaper. Madrid’s father mined coal, and her brother drilled for oil and gas. “If you look at the map, it’s a trip. Just out of nowhere, there’s this giant red spot,” Madrid said. “The data show such high levels of methane. Is that naturally occurring, or is it something we’re doing to the environment?”
Frankenberg still speaks with nostalgia about the lost satellite and the promise it held. A Japanese satellite tracks methane from space, but doesn’t produce the same type of images like the old satellite did. Meanwhile, Europe is scheduled to launch a new satellite instrument in 2016 that will measure methane, ozone, and other gases in the atmosphere with more precision. He hopes the new data will pick up where SCIAMACHY left off. “With satellites, you have global coverage,” Kort said. “There’s a real power in that. You can look in places you didn’t know you needed to look.”

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)


