Text credit: Rob Gutro, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md. (source)
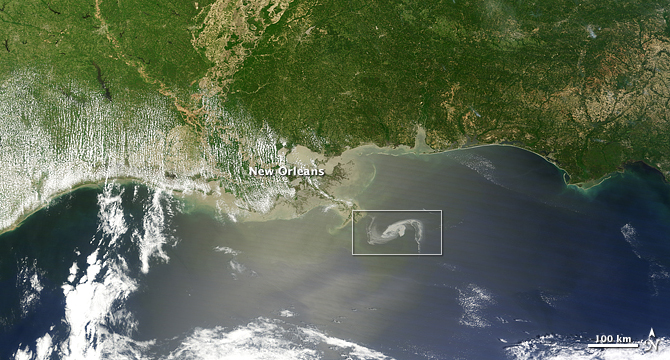
NASA’s Terra satellite flew over the Deepwater Horizon rig’s oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico on Saturday, May 1 and captured a natural-color image of the slick from space. The oil slick resulted from an accident at the Deepwater Horizon rig in the Gulf of Mexico.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument on NASA’s Terra satellite captured a natural-color image. The oil slick appeared as a tangle of dull gray on the ocean surface, made visible to the satellite sensor by the sun’s reflection on the ocean surface. On May 1, most of the oil slick was southeast of the Mississippi Delta.
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) is the lead agency on oil spills and uses airplane fly-over’s to assess oil spill extent. NASA’s Terra and Aqua satellites are also helping NOAA with satellite images of the area.
On Sunday, May 2, NOAA restricted fishing in federal waters of the Gulf of Mexico from the mouth of the Mississippi to Pensacola Bay for at least ten days. More details about the closure can be found at: http://sero.nmfs.noaa.gov/. In addition to the federal closure, Louisiana closed vulnerable fisheries in state waters — within three miles of the coast. NOAA noted that anyone wanting to report oil on land, or for general Community and Volunteer Information, please call 1-866-448-5816. To report oiled or injured wildlife, please call 1-800-557-1401.